Detección de una ACL mediante ICMP
Fecha: 17 y 18 de mayo del 2020
Escenario
Este laboratorio visto del lado de un usuario (o un atacante) analiza como detectar si una ACL nos puede estar filtrando
el tráfico hacia un servicio, y visto del lado del administrador, como evitar darle información extra al atacante.
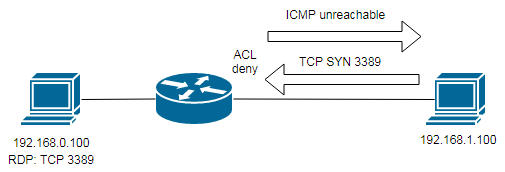
Las pruebas se realizaron solo con lo que tengo en casa por la cuarentena, un router 1841, un servidor RDP en Windows 7
y dos clientes (o atacantes), uno en Windows 10 y otro con Linux para poder ver las interpretaciones diferentes de cada
uno según las pruebas, algunas son similares y otras no, puntualmente una difiere y es la que me interesó documentar.
Este escenario no es de ethical hacking ni de ACL, es para ver los mecanismos de TCP/IP y puntualmente mensajes ICMP.
1.- Verificación inicial:
1.1.
En el
servidor de la aplicación:
C:\>netstat -na
Conexiones activas
Proto Dirección local Dirección remota Estado
TCP 0.0.0.0:135 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:3389 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING (este es el servicio RDP)
TCP 0.0.0.0:5357 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
---resumido---
1.2.- Visibilidad del puerto RDP:
C:\>tcping
192.168.0.100 3389
Probing 192.168.0.100:3389/tcp - Port is open -
time=15.239ms
Probing 192.168.0.100:3389/tcp - Port is open -
time=8.841ms
Probing 192.168.0.100:3389/tcp - Port is open -
time=8.417ms
Probing 192.168.0.100:3389/tcp - Port is open -
time=12.021ms
1.3.- Como es la conversación TCP del TCPing:
Es un handshacking TCP normal de inicio y cierre de sesión por cada línea de TCPing (aquí se muestra solo la primera de cuatro).
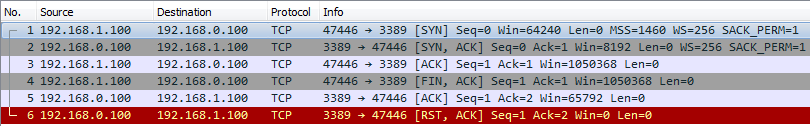
Figura: mikrotik.com
1.4.- Prueba de escaneo Nmap:
C:\Nmap>nmap 192.168.0.100 -p3389 –Pn (-Pn es sin envío previo de ping)
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org
) at 2020-05-17 19:08 Hora estandar de Argentina
Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.100
Host is up (0.00s latency).
PORT
STATE SERVICE
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in
17.26 seconds
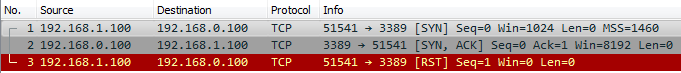
1.5.- Como es la conversación TCP del
Nmap:
Vemos que por default cuando el server responde Nmap detecta puerto abierto y envía un reset para anular la sesión.
2.- Análisis de un servidor con
el servicio RDP apagado:
2.1.- Desactivamos el servicio RDP:
2.2.- Verificación:
C:\>netstat -na
Conexiones activas
Proto Dirección local Dirección remota Estado
TCP 0.0.0.0:135 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING (no muestra el port 3389)
TCP 0.0.0.0:5357 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
---resumido---
2.3.- Verificamos acceso mediante Windows:
Podemos ver que el server envía un TCP RST indicando que el servicio no está disponible (en la jerga sería “se bajó el puerto”).
C:\Nmap>nmap
192.168.0.100 -p3389 -Pn
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org
) at 2020-05-17 19:11 Hora estandar de Argentina
Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.100
Host is up (0.00s latency).
PORT
STATE SERVICE
3389/tcp closed ms-wbt-server
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in
17.21 seconds
![]()
2.4.- Verificamos acceso mediante Linux:
root@kali:~# nmap 192.168.0.100 -p3389 -Pn
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org
) at 2020-05-17 19:11 EDT
Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.100
Host is up (0.0014s latency).
PORT
STATE SERVICE
3389/tcp closed ms-wbt-server
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in
13.13 seconds
![]()
3.- Con RDP filtrado:
Ahora comenzamos a experimentar con una ACL que bloquee el puerto 3389 para ver las diferencias con el “puerto abajo”
del punto anterior, asumimos que el servicio RDP se encuentra “arriba nuevamente”.
3.1.- Agregamos una ACL para filtrar el puerto de RDP:
Router#conf
t
Router(config)#access-list 100 deny tcp
192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 eq 3389 (creamos el filtro)
Router(config)#int fa0/1
Router(config-if)#ip access-group 100 in (lo asociamos a la interface que “mira” al
cliente)
Router(config-if)#end
Router#
3.2.-
Verificamos acceso mediante Windows:
C:\Nmap>nmap
192.168.0.100 -p3389 -Pn
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org
) at 2020-05-17 19:16 Hora estandar de Argentina
Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.100
Host is up (0.00s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE
3389/tcp filtered ms-wbt-server (en las pruebas anteriores decía closed)
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in
17.20 seconds

3.3.- Verificamos acceso mediante Linux:
root@kali:~# nmap 192.168.0.100 -p3389 -Pn
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org
) at 2020-05-17 19:16 EDT
Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.100
Host is up (0.0012s latency).
PORT
STATE SERVICE
3389/tcp filtered ms-wbt-server
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in
13.12 seconds

Frame 2: 70 bytes on
wire (560 bits), 70 bytes captured (560 bits) on interface 0
Ethernet II, Src: 00:17:95:c0:ac:a3,
Dst: 08:00:27:7c:8e:8e
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 192.168.1.1, Dst: 192.168.1.101
Internet Control
Message Protocol
Type: 3 (Destination
unreachable) (ver tabla de tipos ICMP)
Code: 13 (Communication
administratively filtered) (nos está indicando que fué filtrado)(ver tabla de códigos)
Checksum: 0x72ae [correct]
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 192.168.1.101, Dst:
192.168.0.100
Total Length: 44
Identification: 0x35bf (13759)
Flags: 0x0000
Time to live: 40
Protocol: TCP (6)
Header checksum: 0xd9f3 [validation disabled]
Source: 192.168.1.101
Destination: 192.168.0.100
Transmission Control Protocol, Src Port: 36338, Dst
Port: 3389
Source Port: 36338
Destination Port: 3389 (nos está indicando en port al que intentamos llegar)
Sequence number: 1842381124
4.- Pruebas con RDP filtrado y sin aviso de filtro:
4.1.- Desactivamos el aviso ICMP:
Desactivamos los mensajes de destino inalcazable (ver tabla de tipos y códigos ICMP).
Router#conf t
Router(config)#int fa0/1
Router(config-if)#no ip unreachables
Router(config-if)#end
Router#
4.2.-
Verificamos acceso mediante Windows:
C:\Nmap>nmap
192.168.0.100 -p3389 -Pn
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org
) at 2020-05-17 19:21 Hora estandar de Argentina
Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.100
Host is up.
PORT
STATE SERVICE
3389/tcp filtered ms-wbt-server (podemos ver que el mensaje es el mismo, al no recibir mensajes con un
motivo específico Nmap asume el host
como UP)
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 19.25 seconds

4.3.- Verificamos acceso mediante Linux:
root@kali:~# nmap 192.168.0.100 -p3389 -Pn
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org
) at 2020-05-17 19:21 EDT
Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.100
Host is up.
PORT
STATE SERVICE
3389/tcp filtered ms-wbt-server
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 15.13 seconds

5.- Pruebas con ping y con aviso de filtrado:
5.1.- Agregamos una línea más a la ACL existente:
Aunque la ACL tiene un deny ip any any implícito la agregamos con motivos gráficos para ver los matches.
Router#conf
t
Enter configuration commands, one per
line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#access-list 100 deny icmp any any
Router(config)#
En esta prueba se encuentra activado ip unreachables en la interface Fa0/1.
Router(config)#int fa0/1
Router(config-if)#ip unreachables
Router(config-if)#end
Router#
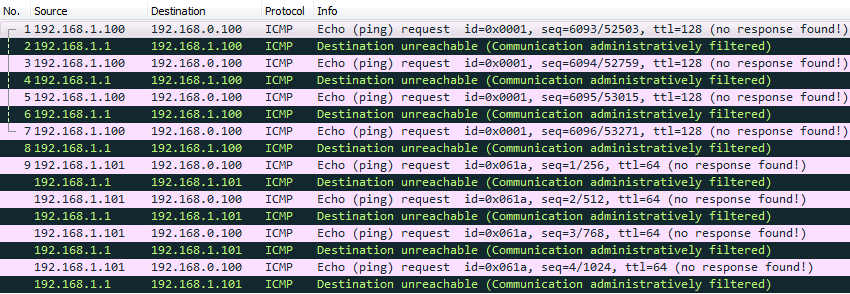
5.2.- Verificamos acceso mediante Windows:
C:\>ping 192.168.0.100
Haciendo ping a 192.168.0.100 con 32 bytes de datos:
Respuesta desde 192.168.1.1: Red de destino inaccesible. (no nos da el motivo)
Respuesta desde 192.168.1.1: Red de destino inaccesible.
Respuesta desde 192.168.1.1: Red de destino inaccesible.
Respuesta desde 192.168.1.1: Red de destino inaccesible.
5.3.- Verificamos acceso mediante Linux:
root@kali:~# ping 192.168.0.100
PING 192.168.0.100 (192.168.0.100) 56(84) bytes of data.
From 192.168.1.1 icmp_seq=1 Packet filtered (esto es lo que interesa diferenciar de Windows, nos da un indicio de filtrado a nivel usuario)
From 192.168.1.1 icmp_seq=2 Packet filtered
From 192.168.1.1 icmp_seq=3 Packet filtered
From 192.168.1.1 icmp_seq=4 Packet filtered
6.- Pruebas con ping sin aviso de filtrado:
6.1.- Desactivamos ip unreachables en la interface Fa0/1:
Router#conf
t
Router(config)#int fa0/1
Router(config-if)#no ip unreachables
Router(config-if)#end
Router#
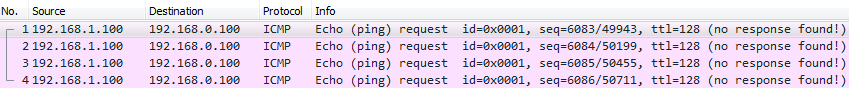
6.2.- Verificamos acceso mediante Windows:
C:\>ping 192.168.0.100
Haciendo ping a 192.168.0.100 con 32 bytes de datos:
Tiempo de espera agotado para esta solicitud.
Tiempo de espera agotado para esta solicitud.
Tiempo de espera agotado para esta solicitud.
Tiempo de espera agotado para esta solicitud.
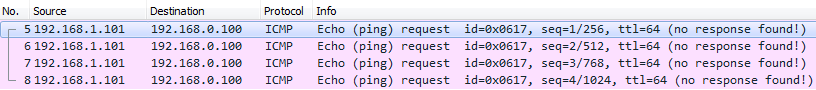
6.3.- Verificamos acceso mediante Linux:
root@kali:~# ping 192.168.0.100 (Linux no muestra respuestas negativas)
PING 192.168.0.100 (192.168.0.100)
56(84) bytes of data.
^C
--- 192.168.0.100 ping statistics ---
9 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 8170ms
6.4.- Verificación en la ACL:
Router#sh access-list
Extended IP access list 100
10 deny
tcp 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 eq 3389 (32 matches)
20 deny icmp any any (16 matches) (este es el motivo gráfico, para ver los matches, de lo contrario no se contabilizan)
Router#
7.- Configuración del router:
Router#sh runn (solo lo mas
relevante)
Building configuration...
Current configuration :
1038 bytes
!
version 12.4
!
hostname Router
!
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/1 (no nos muestra ip unreachables porque está por default)
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip access-group 100 in
!
!
access-list 100 deny tcp 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.0.0
0.0.0.255 eq 3389
access-list 100 deny icmp any any
!
end
Router#
8.- Para verificar la aplicación o no de ip unreachables en la
interface:
8.1.-
Activado:
Router#sh
ip interface fa0/1
FastEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up
Internet address is
192.168.1.1/24
Broadcast address is
255.255.255.255
Address determined by
non-volatile memory
MTU is 1500 bytes
Helper address is not set
Directed broadcast forwarding is
disabled
Outgoing access list is not set
Inbound access list is 100
Proxy ARP is enabled
Local Proxy ARP is disabled
Security level is default
Split horizon is enabled
ICMP redirects are always sent
ICMP unreachables are always sent (activado)
ICMP mask replies are never sent
IP fast switching is enabled
IP fast switching on the same
interface is disabled
IP Flow switching is disabled
IP CEF switching is enabled
IP CEF Feature Fast switching
turbo vector
IP multicast fast switching is
enabled
IP multicast distributed fast
switching is disabled
IP route-cache flags are Fast,
CEF
Router Discovery is disabled
IP output packet accounting is
disabled
IP access violation accounting
is disabled
TCP/IP header compression is
disabled
RTP/IP header compression is
disabled
Policy routing is disabled
Network address translation is
disabled
BGP Policy Mapping is disabled
WCCP Redirect outbound is
disabled
WCCP Redirect inbound is
disabled
WCCP Redirect exclude is
disabled
Router#
8.2.-
Desactivado:
Router#sh
ip interface fa0/1
FastEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up
Internet address is
192.168.1.1/24
Broadcast address is
255.255.255.255
Address determined by
non-volatile memory
MTU is 1500 bytes
Helper address is not set
Directed broadcast forwarding is
disabled
Outgoing access list is not set
Inbound access list is 100
Proxy ARP is enabled
Local Proxy ARP is disabled
Security level is default
Split horizon is enabled
ICMP redirects are always sent
ICMP unreachables are never sent (desactivado)
ICMP mask replies are never sent
IP fast switching is enabled
IP fast switching on the same
interface is disabled
IP Flow switching is disabled
IP CEF switching is enabled
IP CEF Feature Fast switching
turbo vector
IP multicast fast switching is
enabled
IP multicast distributed fast
switching is disabled
IP route-cache flags are Fast,
CEF
Router Discovery is disabled
IP output packet accounting is
disabled
IP access violation accounting
is disabled
TCP/IP header compression is
disabled
RTP/IP header compression is
disabled
Policy routing is disabled
Network address translation is
disabled
BGP Policy Mapping is disabled
WCCP Redirect outbound is
disabled
WCCP Redirect inbound is
disabled
WCCP Redirect exclude is
disabled
Router#
9.- Detalle de los mensajes ICMP:
9.1.-
Códigos ICMP:
0 Echo Reply
1 Unassigned
2 Unassigned
3 Destination Unreachable
4 Source Quench
(Deprecated)
5 Redirect
6 Alternate Host
Address (Deprecated)
7 Unassigned
8 Echo
9 Router Advertisement
10 Router
Solicitation
11 Time Exceeded
12 Parameter Problem
13 Timestamp
14 Timestamp Reply
--- resumido (deprecated) ---
19 Reserved (for
Security)
20-29 Reserved (for Robustness
Experiment)
--- resumido (deprecated) ---
255 Reserved
9.2.- Dentro del type 3:
0 Net Unreachable
1 Host Unreachable
2 Protocol
Unreachable
3 Port Unreachable
4 Fragmentation Needed and Don't Fragment was Set
5 Source Route Failed
6 Destination Network
Unknown
7 Destination Host
Unknown
8 Source Host Isolated
9 Communication with
Destination Network is Administratively Prohibited
10 Communication with
Destination Host is Administratively Prohibited
11 Destination Network
Unreachable for Type of Service
12 Destination Host
Unreachable for Type of Service
13 Communication Administratively
Prohibited
14 Host Precedence
Violation
15 Precedence cutoff in
effect
Fuente: iana.org
(2020) Networking
for alien minds
Rosario, Argentina